Mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can significantly impact an individual’s well-being and quality of life. While traditional therapeutic approaches have proven effective, the integration of complementary therapies, such as hypnosis, offers a unique and powerful tool for treating these conditions. In this article, we will explore the effectiveness of hypnosis in addressing mental health conditions, highlighting its benefits as a complementary therapy alongside traditional treatment modalities.
Understanding Hypnosis
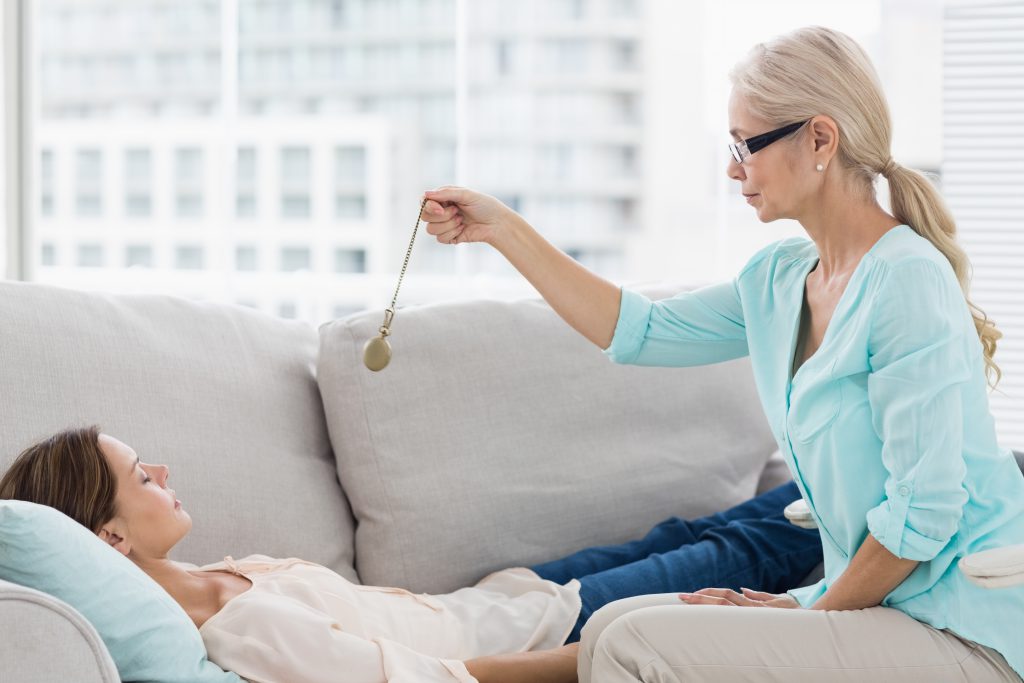
Hypnosis is a state of focused attention and heightened suggestibility, in which an individual enters a trance-like state that allows for increased receptivity to positive suggestions and therapeutic interventions. When guided by a skilled therapist, hypnosis can access the subconscious mind, where deeply ingrained beliefs and emotional patterns reside. By identifying and restructuring these patterns, hypnosis can foster positive change, enhance coping mechanisms, and alleviate symptoms associated with mental health conditions.
The Efficacy of Hypnosis in Anxiety Management
Anxiety disorders, characterized by excessive worry, fear, and physical symptoms, affect millions of individuals worldwide. Research has shown that hypnosis can effectively reduce anxiety symptoms by inducing a deep state of relaxation, calming the mind, and providing individuals with tools for managing stressful situations. Hypnosis has been particularly effective in treating specific phobias, social anxiety, and generalized anxiety disorder.
The Role of Hypnosis in Treating Depression
Depression, marked by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest, is a prevalent mental health condition. While medication and talk therapy remain key components of treatment, hypnosis can play a valuable role in adjunctive care. Hypnosis for depression aims to identify and reframe negative thought patterns and beliefs, promote emotional resilience, and facilitate the development of positive coping strategies. Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of hypnosis in reducing depressive symptoms and enhancing overall well-being.
Hypnosis for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Recovery
PTSD, often triggered by a traumatic event, can severely impact individuals’ lives, leading to intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, and heightened anxiety. Hypnosis has garnered attention as a complementary therapy for PTSD recovery, assisting individuals in processing traumatic memories and reducing the emotional and physical distress associated with the disorder. By gently guiding individuals through the reintegration of traumatic experiences, hypnosis empowers individuals to regain control over their emotions and promote healing.
Complementary Benefits of Hypnosis
One of the significant advantages of hypnosis as a complementary therapy is its versatility and ability to address the underlying issues that contribute to mental health conditions. Hypnosis techniques can help individuals uncover root causes, release emotional blockages, and develop new patterns of thinking and behavior. Moreover, hypnosis empowers individuals by providing them with a sense of agency and control over their mental health, fostering self-efficacy and resilience.
Integrating Hypnosis with Traditional Therapy Approaches
While hypnosis offers unique benefits, it is essential to emphasize its role as a complementary therapy. Collaborative efforts between hypnotherapists and other mental health professionals are crucial to ensure comprehensive and individualized care. By integrating hypnosis with traditional therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or psychoanalysis, individuals can maximize their treatment outcomes and address a broader range of factors contributing to their mental health conditions.
Ethical Considerations and Precautions
As with any therapeutic modality, ethical considerations and precautions must be adhered to when using hypnosis in mental health treatment. Informed consent, client autonomy, and the therapist’s qualifications and ethical standards are essential factors for ensuring responsible and effective hypnotherapy. Additionally, hypnosis should not replace conventional treatment methods but rather serve as a complementary approach for holistic care.
Conclusion
The integration of hypnosis into mental health treatment holds significant promise for individuals combating anxiety, depression, and PTSD. By harnessing the power of the subconscious mind, hypnosis provides an additional avenue for healing, growth, and symptom reduction. The evidence supporting the efficacy of hypnosis in mental health treatment is growing, highlighting the importance of collaborative efforts between hypnotherapists and mental health professionals. By embracing hypnosis as a powerful tool in therapy, individuals can unlock their inner resources, overcome barriers, and embark on a journey of profound healing and transformation.